FUNCTIONAL DESCRIPTION
 A sampling system is required for sampling the aerosols in the 135-32 km and 22-17 km altitude regions of Titan's atmosphere. These altitude ranges refer to the Probe's nominal descent profile (Lebreton & Matson, 1997).
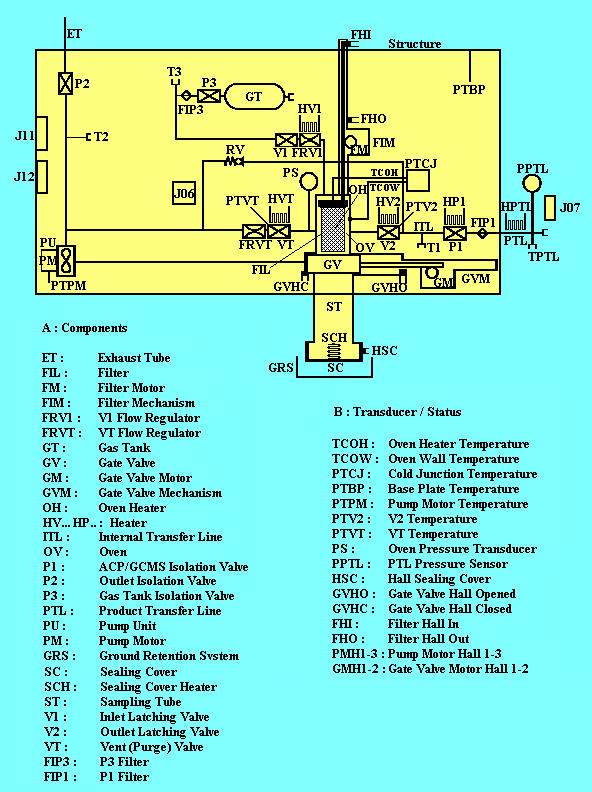
The sampling system requires an inlet (sampling) tube (ST) extending beyond the boundary layer (estimated to be few mm thick): the end protrudes 28 mm from the Probe's fore dome.
A sampling system is required for sampling the aerosols in the 135-32 km and 22-17 km altitude regions of Titan's atmosphere. These altitude ranges refer to the Probe's nominal descent profile (Lebreton & Matson, 1997).
The sampling system requires an inlet (sampling) tube (ST) extending beyond the boundary layer (estimated to be few mm thick): the end protrudes 28 mm from the Probe's fore dome.
During sampling, the collecting target's temperature must be as close as possible to that of Titan's atmosphere in order to help retain the more volatile aerosol and cloud particle components. The target is a filter (FIL), made in stainless steel (Beckaert ST10), that can be moved along the inlet tube.
A pump unit (PU) is used to force the gas flow through the filter. In its sampling position, the filter front face extends a few mm beyond the inlet tube. This increases aerosol collection by the way of direct impaction at high altitude, when the pump is not yet efficient.
Before descent, the filter is held in its storage position inside the oven (OV). During descent, a mechanism (FIM) can move the filter to its sampling position and return it into the oven.
The oven is a pyrolysis furnace where a heating element (OH) can heat the filter and hence the sampled aerosols to 250°C or 600°C. A motorised gate valve (GV) can be activated to close the furnace after filter retraction.
Three normally-closed monostable valves (V1, V2, VT) are mounted on the oven's body. V1 supplies a labelled gas (IsN2) to carry the gas sample from the oven to the transfer lines through V2. The venting valve VT allows the oven's gas content to be vented to Titan's atmosphere. VT is also usually activated during certain sequences for purging operations or under pressure control before transfers (see below). Also, VT can be opened at any time during descent as a safety measure if the oven pressure rises above 3.2 bar; it closes when the pressure falls to 2.7 bar.
The pump unit (PU) is a drag fan which accelerate the flow of Titan's atmosphere at a rate depending on altitude. An exhaust tube (ET), with a one-shot isolation valve (P2), allows the gas to be vented externally. The gas flow, on reaching the level of the GV, follows a path perpendicular to the oven/GV assembly. The result is that the circulation is independent of the GV status (closed or open). When it is switched off, PU acts as a flow-blocking device.
The pressurisation system for storing N2 gas and controlling its flow to the oven begins with a gas tank (GT) at 40 bar. Oven filling is controlled by a pressure transducer (PS) associated with valve Vl.
A relief valve (RV, set at 4.1 bar) in the internal gas transfer line protects GCMS against accidental ACP overpressure.
The whole internal circuit is pressurised during ground operations and the early part of the flight to Saturn. After the Jupiter flyby, about 3 years after launch, ACP's internal circuit is evacuated by opening P2. In addition, valves V1, V2 and VT are opened briefly during each cruise phase checkout. The gate valve mechanism (GVM) is locked during launch, and unlocked shortly after. It must be locked again for a short time before Probe entry; this is done during the last cruise checkout sequence.
The inlet tube end is closed by a sealing cover (SC), which will be opened at the beginning of descent. A connecting tube (Product Transfer Line, PTL) between ACP and GCMS transfers the pyrolysis products. Valve Pl isolates the ACP internal circuit from the product transfer lines. This one-shot isolation valve is opened at the beginning of descent (To+2 min) for an initial venting of the internal (ITL) and the external (PTL) exit transfer lines. The IVA one-shot valve isolates the PTL at its GCMS extremity. The T1, T2 and T3 special ports are for ground tests. The V2 and VT electrovalves, Pl and PTL can be heated by special heaters (HV1 for V1, HV2 for V2, HVT for VT, HP1 for P1 and HPTL for PTL). In addition, heater HV1 is controlled by a thermostat, activated when the temperature falls below -5°C. This prevents leakage caused by Titan's low temperatures.
 A sampling system is required for sampling the aerosols in the 135-32 km and 22-17 km altitude regions of Titan's atmosphere. These altitude ranges refer to the Probe's nominal descent profile (Lebreton & Matson, 1997).
The sampling system requires an inlet (sampling) tube (ST) extending beyond the boundary layer (estimated to be few mm thick): the end protrudes 28 mm from the Probe's fore dome.
A sampling system is required for sampling the aerosols in the 135-32 km and 22-17 km altitude regions of Titan's atmosphere. These altitude ranges refer to the Probe's nominal descent profile (Lebreton & Matson, 1997).
The sampling system requires an inlet (sampling) tube (ST) extending beyond the boundary layer (estimated to be few mm thick): the end protrudes 28 mm from the Probe's fore dome.
 Measurement Strategy & Operation Sequences
Measurement Strategy & Operation Sequences
 Back to ACP home page
Back to ACP home page